If properly leveraged, natural climate solutions can contribute over 37% of cost-effective CO2 mitigation by 2030. Evidence shows Indigenous Peoples and local communities are key to achieving such outcomes. This report presents the most comprehensive assessment to date of carbon storage in documented community lands worldwide.

At a Crossroads: Consequential Trends in Recognition of Community-Based Forest Tenure from 2002-2017
This analysis reports on trends in global forest tenure from 2002-2017. It is the fourth in a series of analyses monitoring the legal recognition of forest tenure around the world.
Despite widespread poverty and insecure resource rights, evidence shows that Indigenous Peoples and local communities are still spending their limited resources on conservation efforts. They are also achieving outcomes that are at least equivalent to those of government-funded protected areas. This brief shows an urgent need to replace the fortress-conservation model with rights-based approaches to both improve conservation outcomes and end human-rights abuses committed in the name of conservation.
This brief presents a review of the nominal progress made in the national-level laws and regulations that govern the carbon trade and define the rights of parties—across a sample of 24 countries in Africa, Asia and Latin America. These countries collectively hold more than 50 percent of global tropical and subtropical forests.
This study assesses the cumulative risks and impacts of all REDD+ initiatives in the DRC province of Mai-Ndombe on the rights and subsistence of local communities and Indigenous Peoples. Using existing tools while taking into account gray areas in the REDD+ process, the study maps all existing and planned REDD+ initiatives in the province.
The purpose of this report is to situate existing knowledge on First Nation-held forestry tenures and community forest enterprises (CFEs) in British Columbia, Canada within a broader discussion about Indigenous and non-Indigenous community forests in Canada.
Drawing on international standards and Green Climate Fund policy documents, this report traces the adequacy and implementation effectiveness of the Fund’s current institutional frameworks across a representative sample of approved projects. Noting critical gaps in nearly every aspect of the Fund’s operational modalities and project approval processes, the report calls on the GCF to take progressive steps to make Indigenous Peoples’ and local communities’ rights a key part of its climate actions going forward.
This report highlights FRA’s potential in transforming forest governance by empowering local communities and the gram sabha to protect and conserve forests; ensuring livelihood security and poverty alleviation; securing gender justice; meeting SDG, especially the goals of eliminating poverty and achieving ecological sustainability; and dealing with climate change.
Compelling quantitative evidence of the unparalleled role that forest peoples have to play in climate change mitigation.
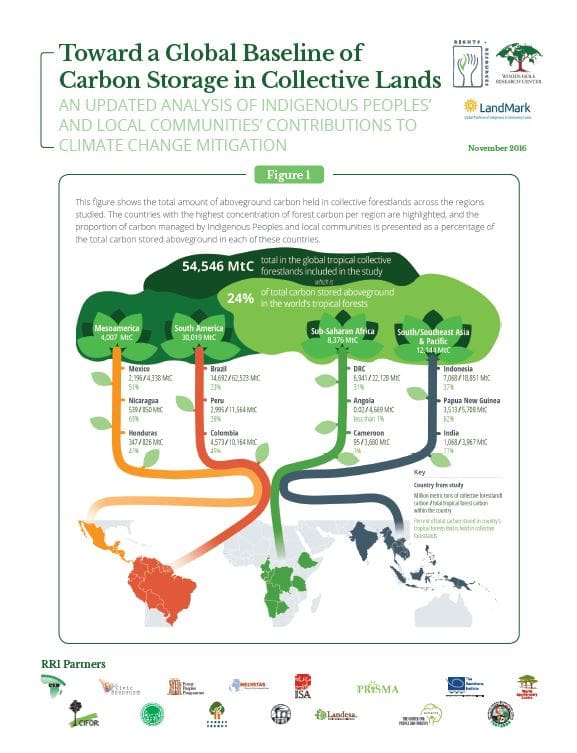
A new report quantifying the carbon stored aboveground in tropical forests that are legally owned or traditionally held by Indigenous Peoples and local communities in 37 countries across tropical America, Africa, and Asia.
Between June and August 2016, the Colombian government made two announcements that will profoundly change the country. After four years of peace negotiations with the FARC guerillas,…
New research from RRI reveals that 13 submissions to the World Bank’s Carbon Fund–one of the most advanced REDD+ initiatives–either fail to recognize the importance of land rights or adequately include local peoples in key decision-making processes.
A decade after REDD appeared on the international scene, mechanisms to reduce emissions by protecting forests–activities referred to as REDD+–are finally moving from the idea…
The DRC is home to some of the world’s most important forests and biomes, so reducing deforestation quickly and efficiently is an important part of…
A review of submitted Intended Nationally Determined Contributions to determine the extent to which Parties made clear commitments to strengthen or expand the tenure and natural resource management rights of Indigenous Peoples and local communities as part of their climate change mitigation plans.
Just over a decade ago, several forest agency leaders from around the world met in Beijing, China at a conference convened by the Rights and Resources…
This joint-opinion brief is released at the 19th Conference of the Parties to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) in Lima, Peru to…
This brief calculates the cost of securing Indigenous Peoples’ and community rights to the tropical forests where they live, noting that secure land tenure is a prerequisite for the success of climate, poverty reduction and ecosystem conservation initiatives.
Forests and their role in reducing global carbon emissions will get their time in the limelight at next week’s U.N. Climate Summit in New York,…
An analysis of the growing body of evidence linking community forest rights with healthier forests and lower carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from deforestation and forest degradation.
Giving forest communities secure rights to their land is an effective but underused way to limit carbon emissions from deforestation, a report showed on Thursday….
De segunda a sábado, Miguel Ramírez, de 58 anos, acorda às 6h30m e vai para o campo como dezenas de outros moradores de Capulálpam de…
While there were many encouraging pronouncements in 2013—from courts, governments, and some of the world’s largest corporations —unfortunately, progress for community land rights on the ground remains very limited.